Blood Clotting Time Determination by Using Capillary Method ( ब्लड क्लोटिंग टाइम कैसे पता लगाएं
Activated Clotting Time ( ACT) Normal range, Test results and clinical significance by
2.2 Pengertian Clotting Time (CT) Clotting Time adalah waktu yang di perlukan darah untuk membeku atau waktu yang di perlukan saat pengambilan darah sampai saat terjadinya pembekuan. Hal ini menunjukkan seberapa baik platelet berinteraksi dengan dinding pembuluh darah untuk membentuk pembekuan darah. Trombin waktu membandingkan tingkat pasien.

PEMERIKSAAN CLOTTING TIME (CT) MASA PEMBEKUAN DARAH!! Analis Kesehatan YouTube
Blood Clots. Blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury. Typically, your body will naturally dissolve the blood.

Hemostasis · Anatomy and Physiology
Berdasarkan Analisis data menggunakan uji Wilcoxon diperoleh nilai Signifkan P = 0,000 (P< 0,05) maka Ho ditolak dan Ha diterima yang menunjukkan bahwa terdapat perbedaan masa pembekuan darah.

Pemeriksaan Waktu Pembekuan (Clotting Time)
Clotting time is a general term for the time required for a sample of blood to form a clot, or, in medical terms, coagulate. The term "clotting time" is often used when referring to tests such as the prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or PTT), activated clotting time (ACT), thrombin time (TT), or Reptilase time.

Blood Clotting time determination by Slide Method YouTube
It's rare that your test will show an abnormally short clotting time. If it does, it may be a sign of increased risk for blood clots (thrombosis), bleeding, or multiple miscarriages. If this test is done because you are taking heparin to help prevent blood clots, your healthcare provider will often want the aPTT to be about 2 to 2.5 times as.

Clotting Time Procedure Physiology Practicals YouTube
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is the time it takes for a patient's blood to form a clot as measured in seconds. It is used to measure the activity of the intrinsic pathway of the clotting cascade. PTT tests the function of all clotting factors except factor VII (tissue factor) and factor XIII (fibrin stabilizing factor). PTT is commonly used in clinical practice to monitor patient response.

PPT Coagulation Time of whole blood PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6134102
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test also measures the speed of clotting but differs from the PT test in that it aims to establish how blood clots within a blood vessel (intrinsic pathway). This is based in part on an enzyme called thromboplastin (clotting factor 11) that converts prothrombin into its more active form, called thrombin.
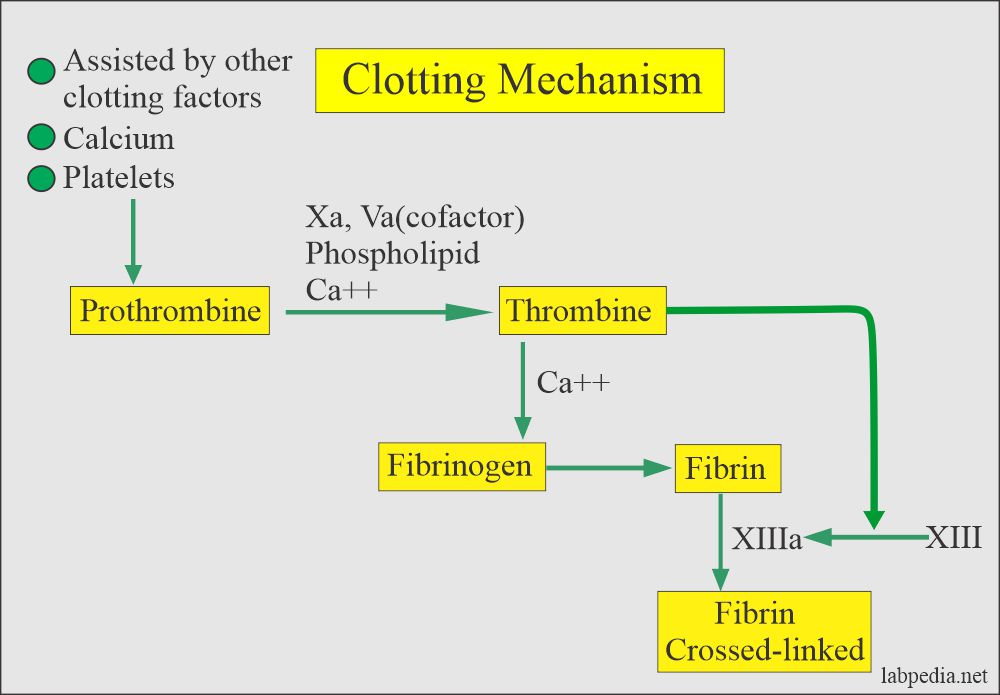
Clotting Time (C T)
The prothrombin time test also may be performed to check for liver disease. It is one of many tests used to screen people waiting for liver transplants. That screening — known as the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) — is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease. If your provider suspects you have other.

PPT BLOOD PowerPoint Presentation ID2058268
Called hematuria, blood in your urine most commonly happens with a bladder infection, prostate infection, or urinary tract stones. These conditions can cause you to pee blood and even form a clot.

PPT Lab Work 3 SDV1 Physiology II Bleeding time, clotting time and BP PowerPoint Presentation
Prothrombin time is one of several blood tests routinely used in clinical practice to evaluate the coagulation status of patients. More specifically, prothrombin time is used to evaluate the extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation, which helps detect deficiencies of factors II, V, VII, and X and low fibrinogen concentrations.[1][2] Prothrombin time measures the time, in seconds, for.

Clotting Time Slide Method YouTube
Blood is a necessary component of the human body, and the loss of this fluid may be life-threatening. Blood is generated via hematopoiesis and ultimately becomes the delivery method for oxygen to the tissues and cells. The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. Vascular mechanisms, platelets, coagulation factors, prostaglandins, enzymes, and proteins are the.

PPT hematology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2758657
A typical PT result is 10 to 14 seconds. Higher than that means your blood is taking longer than normal to clot and may be a sign of many conditions, including: Bleeding or clotting disorder. Lack.
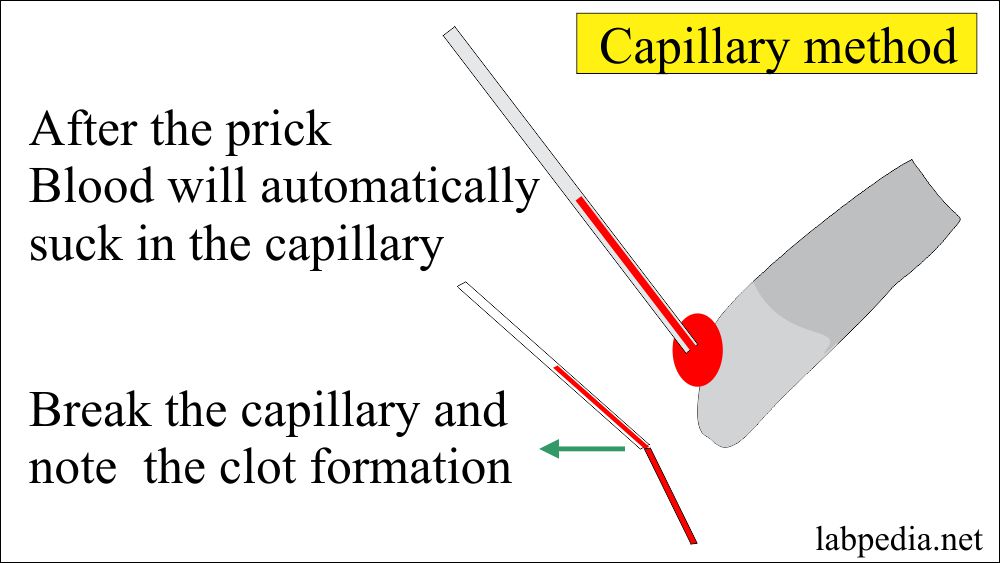
Clotting Time (C T)
Unfractionated heparin (UFH) has been used clinically as an anticoagulant since 1935. 1,2 Thirty-one years later, the activated clotting time (ACT) was developed as a test for the diagnosis and management of patients with inherited coagulation disorders. 3 Later, the ACT test was extensively used to monitor UFH therapy in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery or percutaneous.
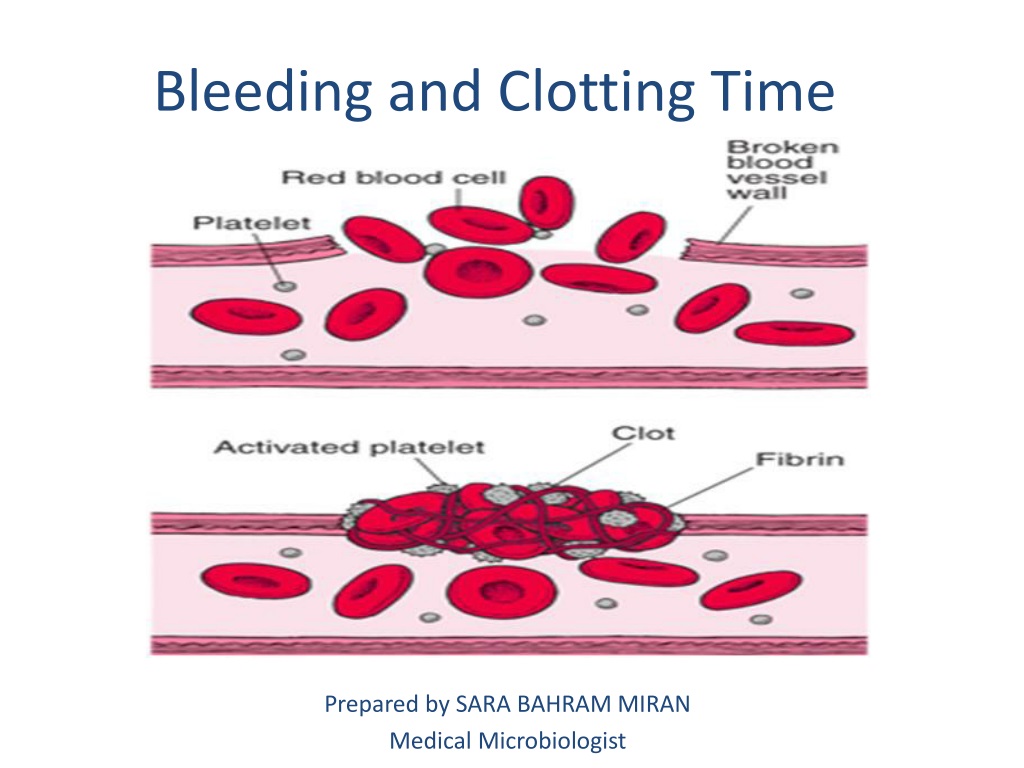
PPT Bleeding and Clotting Time PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9517598
Normalnya, waktu pembekuan darah (clotting time) terjadi dalam 70-120 detik. Namun, jika Anda menjalani terapi antikoagulan, kisaran normalnya adalah 150-600 detik. Abnormal. Darah membutuhkan waktu yang lebih lama untuk membeku, yaitu lebih dari waktu yang disebutkan di atas. Beberapa faktor penyebab di antaranya: penggunaan Heparin,
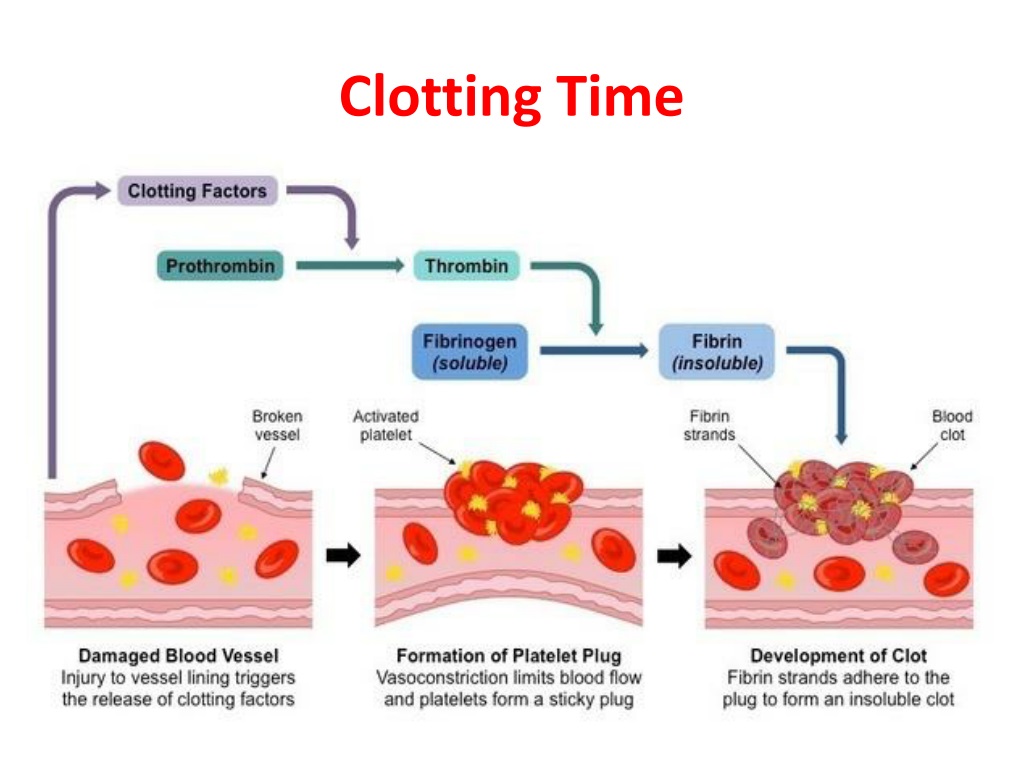
PPT Bleeding and Clotting Time PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9517598
A partial thromboplastin time test or PTT test is a blood test that tells you how long your blood takes to make a blood clot. It takes multiple proteins or clotting factors to complete the clot-making process. If you have an issue with any of these clotting factors, it can affect how long the whole process takes.

Blood Clotting Time Determination by Using Capillary Method ( ब्लड क्लोटिंग टाइम कैसे पता लगाएं
Bookshelf ID: NBK507850 PMID: 29939627. This article is an analysis of the fundamental biochemistry involved in the coagulation cascade, specifically clotting factors and their biochemical interactions and roles among cell membranes, platelets, as proteases, and as cofactors. Other components involved in the process of clot formation will be.