Mengenal Apa Itu Hibridisasi Pengertian Teori Dan Macam Macamnya Kids Images
.jpg)
Hibridisasi Sf4 Brain
Elo bisa coba berlangganan Zenius Aktiva karena ada ratusan soal tentang bentuk molekul mulai dari CO2, SF6, BeCl2 dan beragam bentuk molekul lainya. Klik banner di bawah ya! Sekian materi tentang hibridisasi molekul dari gue, semoga dengan membaca artikel ini elo jadi lebih paham dan bisa mendapat nilai maksimal ketika ujian.

Bentuk molekul 10 SMA (Teori hibridisasi molekul) YouTube
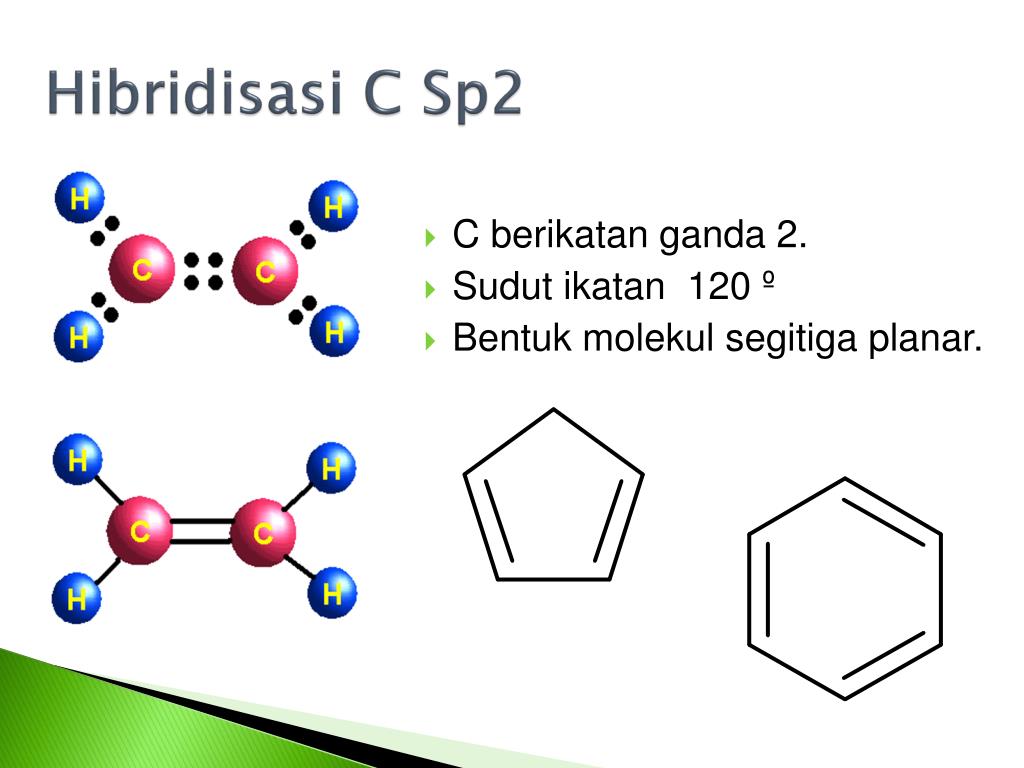
Hibridisasi adalah proses pencampuran orbital-orbital dalam suatu atom. 2. Hanya orbital yang mempunyai energi yang hampir sama besar yang membentuk orbital hibrida. 3. Orbital hibrida yang terbentuk sama banyak dengan jumlah orbital yang bercampur. 4. Dalam hibridisasi yang bercampur adalah jumlah orbital, bukan jumlah elektron. 5.
Menentukan Jenis Hibridisasi, Bentuk Molekul dan Letak Atom O dalam Molekul SOF4 Urip dot Info
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride (British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF 6.It is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable, and non-toxic gas.SF 6 has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule.. Typical for a nonpolar gas, SF 6 is poorly soluble in water but quite soluble in nonpolar.

Hybridization sp3d sp3d2 sp3d3 Formation of PF5, SF6 and IF7 Chemical Bonding
Hello Guys!Today in this video, we are going to learn the hybridization of the SF6 molecules. It is a chemical formula for Sulfur Hexafluoride. To understand.
Perbandingan Jumlah Atom Karbon Dengan Hibridisasi Sp Dan Sp3 Adalah Lengkap
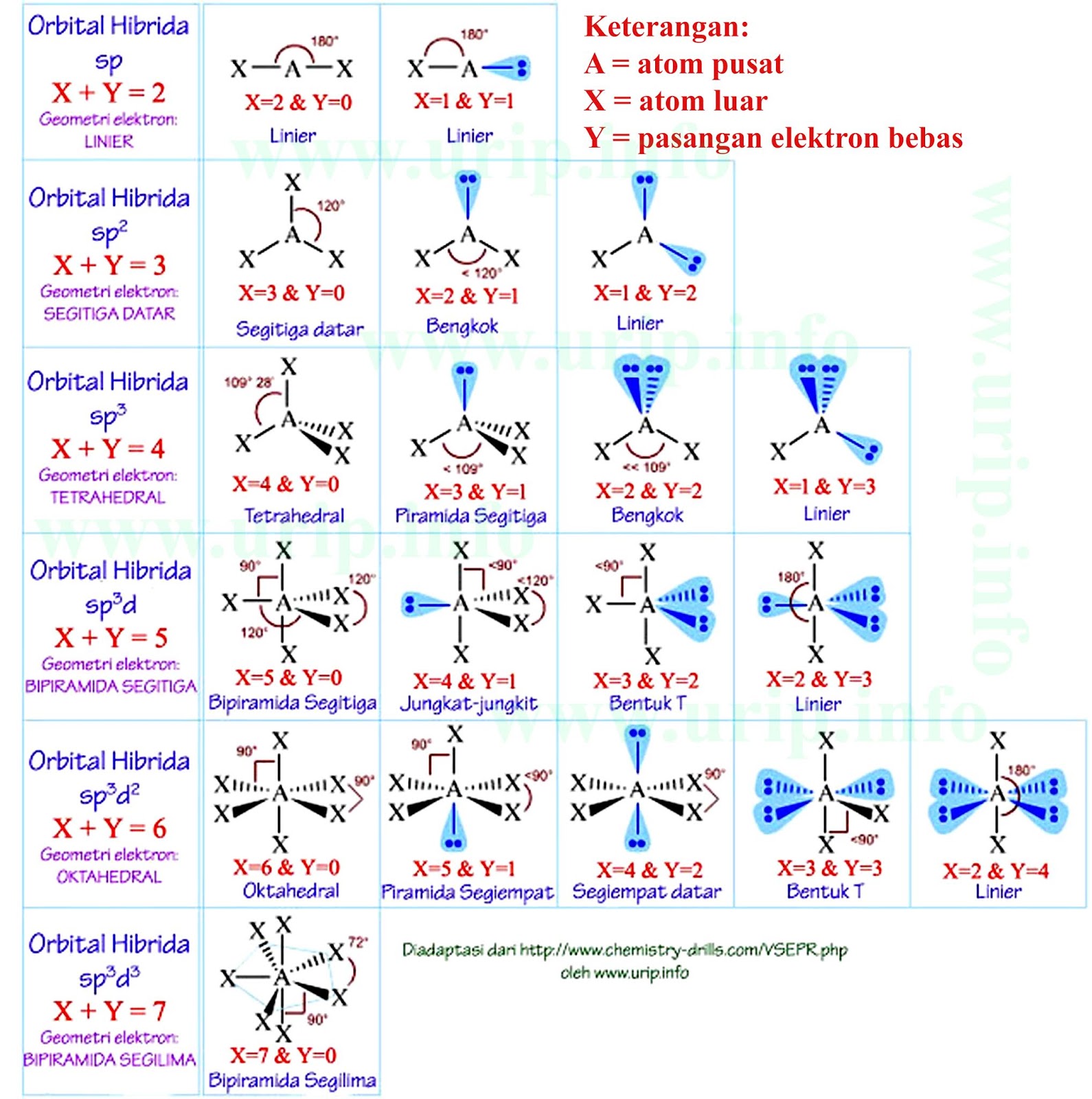
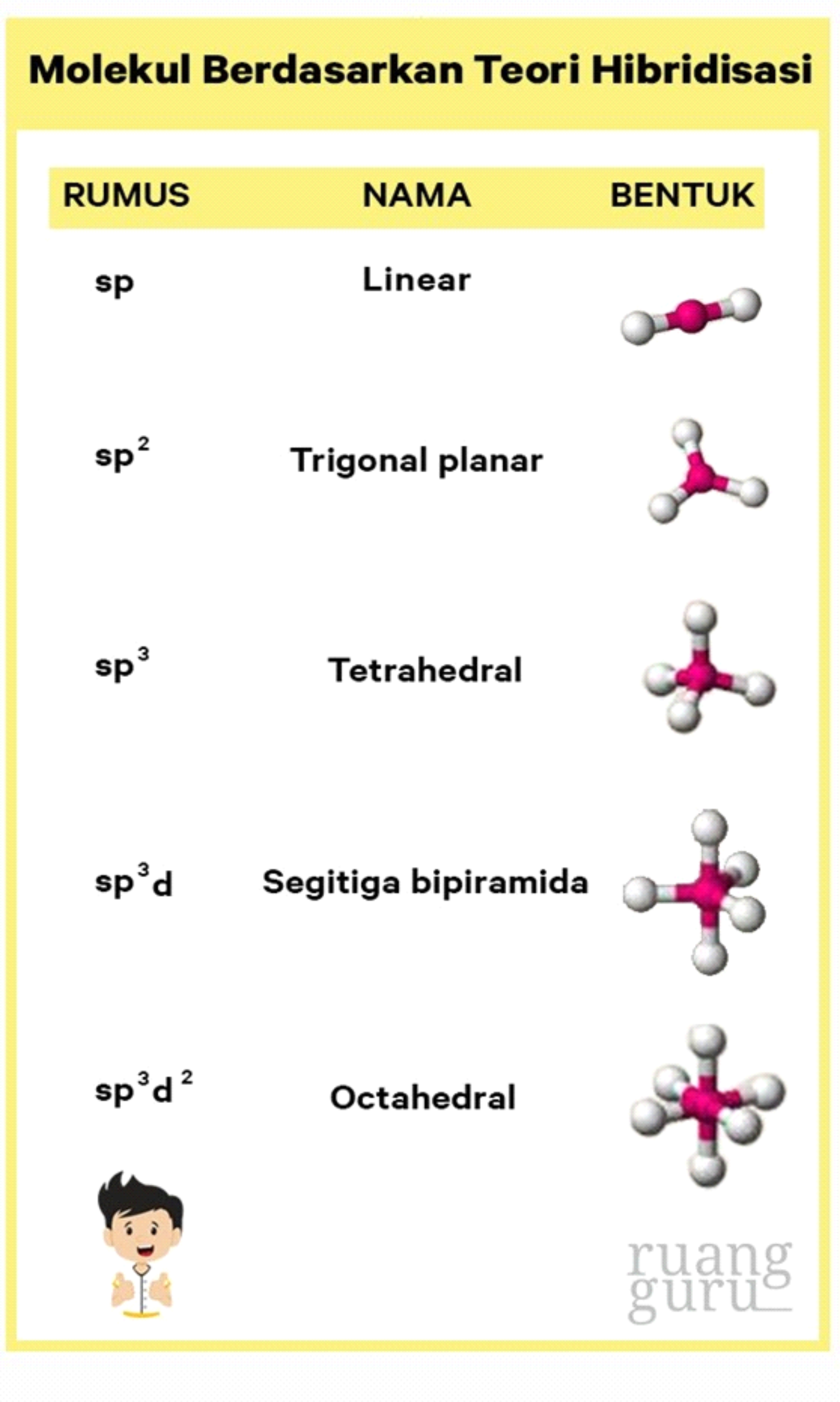
Hibridisasi Kimia Kelas 10 - Pengertian, Tipe, Cara Menentukan, dan Contoh Soal. Hibridisasi adalah proses bergabungnya orbital atom pusat dengan orbital atom lainnya sehingga terbentuk orbital hibrida. Sedangkan bentuk molekul merupakan susunan atom-atom di dalam molekul dalam bentuk tiga dimensi. Artikel ini akan membahas bentuk molekul dan.

Teori Hibridisasi Pelajaran Kimia
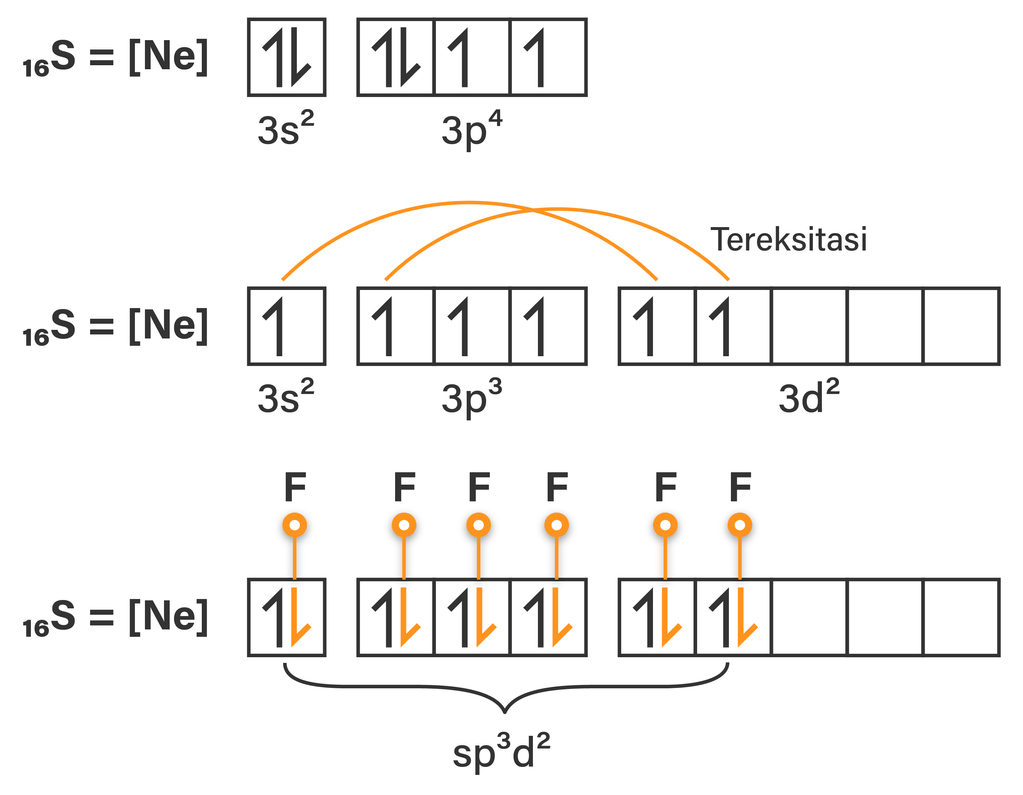
Bentuk hibridisasi dari SF6 (nomor atom S=16) adalah. O Sp3d1 O Sp3d2 O Sp4d3 O Sp3 O Sp2. Untuk menentukan hibridisasi dapat menggunakan 2 cara, berikut adalah uraiannya: Cara 1: 🔸Konfigurasi atom pusat Atom pusat pada senyawa SF₆ adalah unsur S, maka konfigurasi elektronnya adalah ₁₆S = [Ne] 3s² 3p⁴ 🔸 Hibridisasi pada.
Senyawaan Belerang, Ikatan Kimia, Hibridisasi, Bentuk Molekulnya Markas Belajar
sp3d2 Hybridization. In SF6 the central sulphur atom has the ground state outer electronic configuration 3s23p4. In the exited state the available six orbitals i.e., one s, three p and two d are singly occupied by electrons. These orbitals hybridise to form six new sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, which are projected towards the six corners of a regular.
Mengenal Apa Itu Hibridisasi Pengertian Teori Dan Macam Macamnya Kids Images
The Lewis structure of SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) consists of a central sulfur atom bonded to six fluorine atoms.The sulfur atom has six valence electrons, while each fluorine atom contributes one valence electron.; The Lewis structure shows that SF6 has a total of 12 valence electrons, with all atoms achieving an octet configuration.; SF6 is a highly stable and nonpolar molecule due to its.
jelaskan proses hibridisasi molekul SF6...
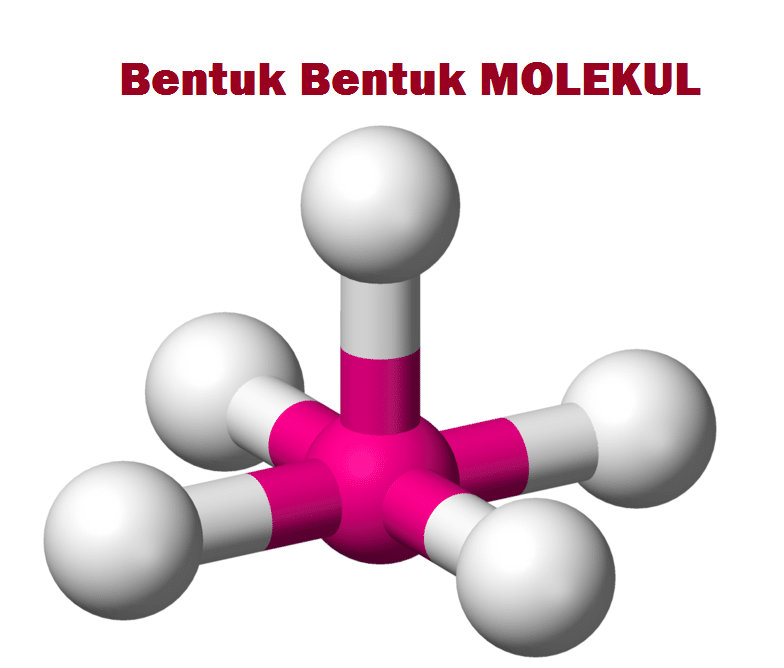
Bentuk molekul salah satunya dapat ditentukan berdasarkan teori hibridisasi. Berdasarkan teori hibridisasi, ada 5 bentuk molekul yaitu: Linear (sp), trigonal planar (sp²), tetrahedral (sp³), segitiga bipiramida (sp³d), dan oktahedral (sp³d²). Dengan demikian, karena hibridisasi SF6 adalah sp³d² maka bentuk molekulnya adalah oktahedral.

Hibridisasi YouTube
Ini sesuai keunikan S yang memiliki subkulit 3d yang kosong. S {-6+6} + 6 (F {-1+1}) ⇒ SF 6. Hibridisasi Atom S, Bentuk Molekul, dan Kepolaran SF2. Detil yang khusus membahas tentang hibridisasi, bentuk molekul, dan kepolaran senyawa silakan disimak di sini. Bentuk dasar (geometri elektron, semua pasangan elektron diperhatikan) SF 2.
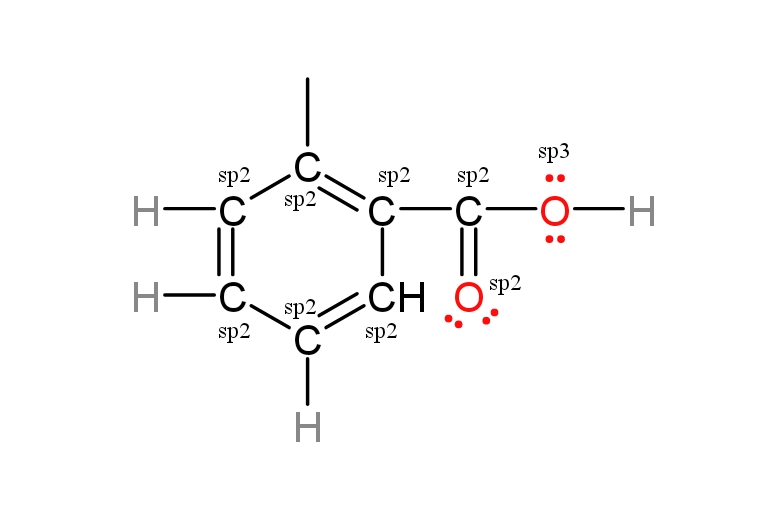
Tentukan hibridisasi dari struktur berikut ini
SF6 (Sulphur Hexafluoride) - Characteristics, Hybridization and Geometry. Sulphur hexafluoride is a non-toxic, non-flammable greenhouse gas that is colorless and odorless. It is inorganic and non-polar. SF6 is normally made by exposing or combining S8 with F2.
Berbagai Bentuk Molekul, Pengertian Teori Domain Elektron Dan Teori Hibridisasi Terlengkap
SF6 is an inorganic colorless greenhouse non-flammable gas with an octahedral geometry in which one sulfur atom is attached with six fluorine atoms. It has an orthorhombic crystalline structure and hypervalent in nature. In SF6, the S-F single bond length is 156.4 pm. ad. Let's focus on the structure, hybridization, formal charge and some.

Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10 • Part 13 Tipe Molekul, Bentuk Molekul, Hibridisasi, dan Kepolaran IF3
Hybridization of SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride) The hybridization of SF 6 is sp 3 d 2 type. Just to describe the compound in brief, Sulphur Hexafluoride is a type of greenhouse gas which is colourless, odourless, non-toxic and non-flammable. It is also an inorganic and non-polar gas. Normally, SF 6 can be prepared by exposing or combining S8 with F2.

Ramalkan Bentuk Molekul Sf 6 Menggunakan Teori Hibridisasi MedArsenal Blog
SF6 Geometry and Hybridization. Sulfur is the central atom: There are 6 + 6×7 = 48 valence electrons, and 12 are taken for making 6 covalent bonds. Each fluorine takes three lone pairs, so there are no electrons left: 48 - (12 + 6×6) = 0. The central atom has 6 atoms connected to it, and no lone pairs, therefore, both geometries are octahedral:

BENTUK MOLEKUL SENYAWA VSEPR dan HIBRIDISASI YouTube
SF6 is a colorless and odorless gas that is non-combustible and non-flammable in nature. The central atom here is sulfur bonded with 6 fluorine atoms. Lewis dot structure has 6 sigma bonds and rests lone pairs on fluorine. The hybridization of SF6 is sp3d2. SF6 has octahedral molecular geometry and is non-polar in nature.

Sf6 Molecule
Orbital hybridisation. In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which.