EventBased Measures of Effect Size ASHA Journals Academy

Como calcular o NNT? Aprendendo com Questões YouTube
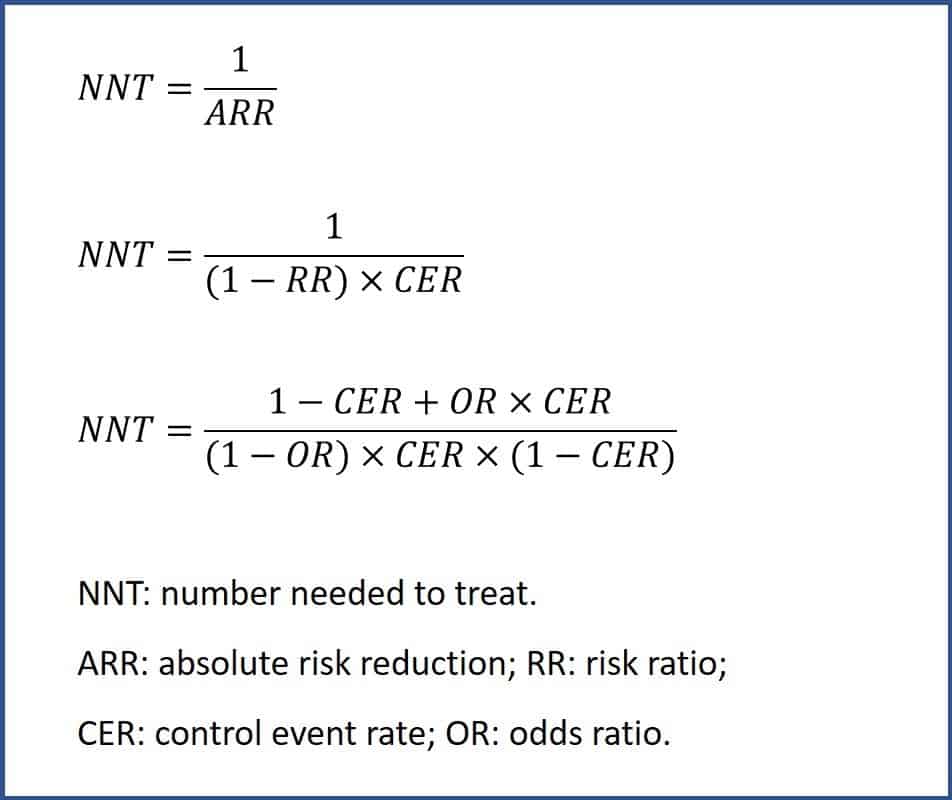
12.5.2 More about the number needed to treat (NNT). The number needed to treat (NNT) is defined as the expected number of people who need to receive the experimental rather than the comparator intervention for one additional person to either incur or avoid an event in a given time frame. Thus, for example, an NNT of 10 can be interpreted as 'it is expected that one additional (or less.
NNT in metaanalysis Science without sense...
If 50/100 had a good outcome in the 50-60 group and 70/100 had a good outcome in the 61-70 group, then the NNT = 1/ (120/200)- (80/200) = 5 people need to be treated with drug x for any improvement in the scale. As with any statistical calculation, there needs to be validation of significance.

28 NNT vs NNH YouTube
Research papers and research summaries frequently present information in the form of derived statistics such as the number needed to treat (NNT) and the number needed to harm (NNH). These statistics are not always correctly understood by the reader. This article explains what NNT and NNH mean; presents a simple, nontechnical explanation for the.

NNT + 4KotA By Tatsuya Shihira NanatsunoTaizai
The relative risk reduction is 1-0.8 = 0.2 or 20% while the absolute risk reduction is 0.4-0.5= .1 or 10%. In this case the relative risk reduction is 20% (much below the RRR for drug X in disease A) while the absolute risk reduction is much higher, 10%. So even though the drug is not very effective, you would still prescribe drug Y in disease.

Number Needed to Treat (NNT) A Quick Tutorial YouTube
A simple transformation of the risk difference known as the number needed to treat (NNT) is a common alternative way of presenting the same information. We discuss NNTs in Section 12.5.2, and consider different choices for presenting absolute effects in Section 12.5.3. We then describe computations for obtaining these numbers from the results.

Number Needed to Treat Thresholding Toolkit
Background. The concept of "number needed to treat" (NNT) was introduced in the medical literature by Laupacis et al. in 1988 [].NNT is an absolute effect measure which is interpreted as the number of patients needed to be treated with one therapy versus another for one patient to encounter an additional outcome of interest within a defined period of time [1, 2].

Chapter 5 The tools of evidencebased medicine European Journal of Hospital Pharmacy
Article Abstract Research papers and research summaries frequently present information in the form of derived statistics such as the number needed to treat (NNT) and the number needed to harm (NNH). These statistics are not always correctly understood by the reader. This article explains what NNT and NNH mean; presents a simple, nontechnical explanation for the calculation of the NNT.

PPT Number Needed to Treat PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4349207
The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad outcome (i.e. the number of patients that need to be treated for one to benefit compared with a control in a clinical trial). It is defined as the inverse of the absolute risk reduction. It was described in 1988. The ideal NNT is 1, where everyone.

[JC Series] Episode 2 Therapy — Pulmcast
The number needed to treat ( NNT) or number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome ( NNTB) is an epidemiological measure used in communicating the effectiveness of a health-care intervention, typically a treatment with medication. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad.

NNT and NNH (1) The Guides
Because decisions regarding therapy are so common in clinical practice, the application of number needed to treat (NNT) is one of the most important evidence-based medicine skills to be acquired. NNT provides a clinically useful "yardstick" of the effort required to have a beneficial outcome or prevent a bad outcome with a therapy. A brief overview of the concept, derivation, and.

Un punto débil. Cálculo del NNT en metanálisis. AnestesiaR
If 8 children out of 100 benefit from treatment, the NNT for one child to benefit is about 13 (100 ÷ 8 = 12.5). For technical reasons, some other measures are often used. The relative risk (RR) of a bad outcome in a group given intervention is a proportional measure estimating the size of the effect of a treatment compared with other.

Number Needed to Treat (NNT) — Why Should You Care About Drug Success Rates
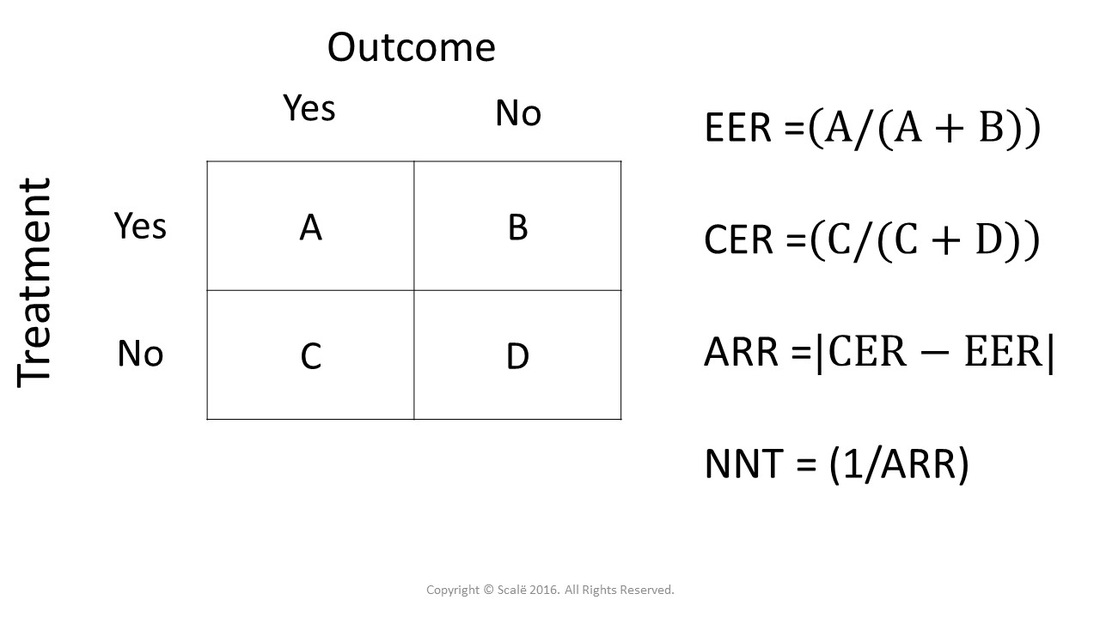
NNT = 1/ARR. Notes: if there was an increase in risk of events in the treatment group compared to the placebo group then: Absolute Risk Increase (ARI) = ART - ARC; Relative Risk Increase (RRI) = ARI / (number of events divided by number of patients receiving active treatment) Reference: Prescribers' Journal (1999), 39 (2), 118-9.
Number Needed to Treat is The Number of People That Have to be Treated to Prevent a Bad
Researchers tested the effectiveness of supplements during pregnancy on pre-eclampsia in a high risk population. A three arm, randomised, blinded, placebo controlled trial design was used. Intervention was two medical food bars a day containing the supplements L-arginine and antioxidant vitamins, antioxidant vitamins alone, or placebo.1 Participants were pregnant women with a previous.

Twitter पर Susan Hopkins "Number Needed to Treat (NNT) and Number Needed to Harm (NNH) are key
Introduction. The number needed to treat (NNT) refers to the average number of patients needed to treat to obtain one response due to treatment. 1 The NNT is a widely used efficacy index in randomised clinical trials. 2 In computing the NNT, it is assumed that the outcome is dichotomous and may be successful or unsuccessful (reflecting treatment responders or non-responders, respectively).

Number Needed to Treat (NNT) How to Calculate and Interpret YouTube
Yang lebih informatif adalah dengan menghitung berapa besar perlakuan yang diujikan memberi perbaikan dibandingkan dengan kontrol, yaitu dengan menghitung relative risk reduction (RRR), atau. • NNT dihitung dengan menggunakan rumus NNT=1/ARR, sehingga didapatkan NNT= 1/0,2 = 5, artinya hanya diperlukan 5 orang yang diberi.

MedAnalisys Relevância. O cálculo do NNT
Number Needed to Treat (NNT) represents the number of patients over a given time period that one would need to treat to achieve one additional study endpoint. As an example, in the PROSEVA trial of patients with severe ARDS, prone positioning decreased 28-day all-cause mortality compared to supine positioning (16% vs. 32.8%) with a NNT of 6.